Abstract
Household displacement following disasters has become endemic in many areas worldwide, affecting at least 265 million people between 2008 and 2018. Although this figure includes short-term and potentially life-saving evacuations, there is ample evidence that not all households return after the emergency phase. Protracted displacement is associated with particularly negative consequences for the affected households and community. Yet, existing data on displacement duration are limited, and only a few disaster recovery models incorporate the multitude of factors beyond housing damage that are known to influence household return. This review synthesizes the current literature on disaster-induced displacement, including key terminology and context, the determinants of household return decisions, existing model-based approaches, and opportunities for future research. The identified key determinants of household return can be broadly organized into the following categories: physical damage to the built environment, psychological and social phenomena (e.g., attachment to place, social networks), household demographics (e.g., tenure, socioeconomic status), and pre- and postdisaster policies (e.g., housing reconstruction approach, design of aid programs).
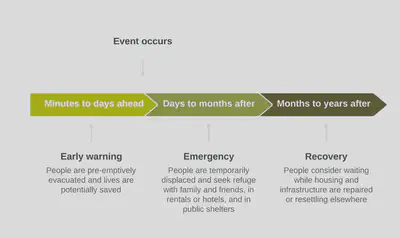
Example figure
Policy documents
- Management of Earthquake Risk in the European Union by the World Bank, 2025
Press
- “Disaster displacement: How growing risks are reshaping resilience” by Willis Towers Watson